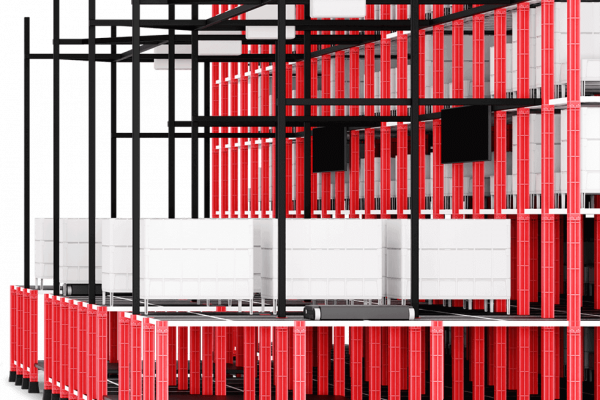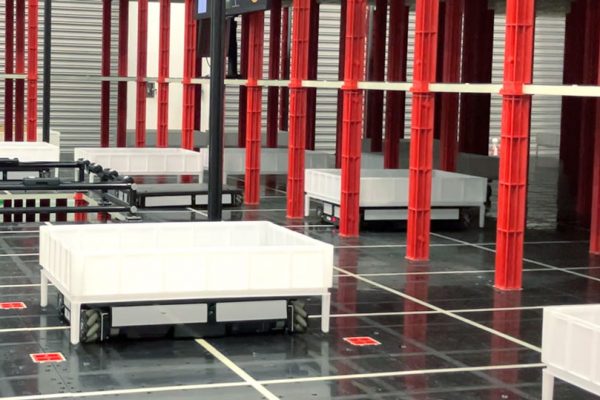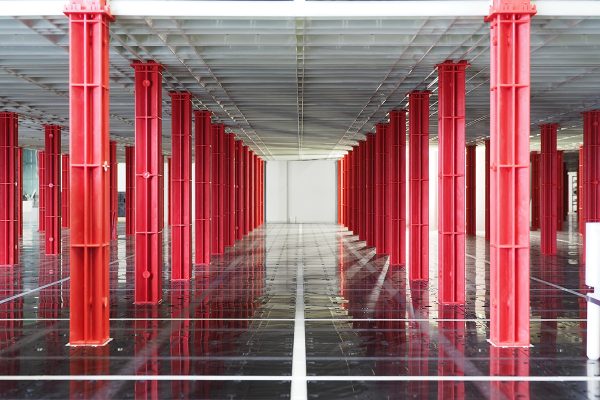
The warehouse and logistics industry are under constant pressure to improve productivity, maximize storage space, and keep up with rising fulfillment demands. Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS) have become a game-changer, enabling warehouses to handle higher volumes with greater speed and accuracy while reducing reliance on manual labor.
However, implementing ASRS comes with its own set of challenges—navigating the complexity of automation, understanding system capabilities, and ensuring seamless integration with existing operations. For warehouse managers and decision-makers, mastering key ASRS terminology is crucial to making informed investment decisions, evaluating system performance, and optimizing warehouse efficiency.
This glossary is designed to be your go-to resource, breaking down essential ASRS-related terms into clear, actionable insights. Whether you’re exploring automation for the first time or upgrading your fulfillment center, this guide will help you make strategic decisions that drive productivity and storage efficiency.
1. Automated Storage and Retrieval System (ASRS)
An Automated Storage and Retrieval System (AS/RS) is a high-tech solution designed to automate the movement of goods within a warehouse, minimizing manual labor, reducing errors, and improving overall efficiency. ASRS uses robotic mechanisms, conveyors, cranes, and software-driven controls to store and retrieve items swiftly and accurately.
This system is particularly useful in high-volume warehouses, e-commerce fulfillment centers, cold storage facilities, and manufacturing environments, where speed, space optimization, and accuracy are critical.
Types of ASRS:
There are multiple types of ASRS solutions, each designed for specific warehouse needs:
1. Unit-Load ASRS
- Handles large, pallet-sized loads using cranes or robotic shuttles.
- Ideal for bulk storage in manufacturing, food & beverage, and industrial warehouses.
- Can store items up to several thousand pounds.
- Improves space utilization by using high-density vertical storage.
2. Mini-Load ASRS
- Designed for smaller cases, totes, or bins.
- Ideal for order fulfillment, spare parts storage, and high-turnover inventory.
- Works with robotic arms and cranes for quick picking.
- Speeds up operations by reducing picker travel time.
3. Shuttle-Based ASRS
- Uses autonomous robotic shuttles that move within racks to store and retrieve goods.
- Ideal for high-density storage and high-speed picking environments.
- Supports scalability—warehouses can add more shuttles to increase capacity.
- Reduces energy consumption and operational costs compared to traditional ASRS.
4. Carousel Systems (Horizontal & Vertical Carousels)
- Horizontal Carousels: Rotating bins that move horizontally, improving access speed for pickers.
- Vertical Carousels: Uses stacked trays that rotate vertically, optimizing vertical space.
- Best suited for small parts storage, pharmaceuticals, and e-commerce fulfillment.
- Reduces picker travel time by delivering items directly to operators.
Each ASRS type can be integrated with WES for enhanced automation, inventory control, and efficiency.
2. Warehouse Execution System (WES)
A Warehouse Execution System (WES) is a real-time software platform that orchestrates warehouse automation by managing inventory, coordinating workflows, and optimizing equipment usage. It serves as the central intelligence that bridges Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and material handling equipment (MHE) like ASRS, conveyors, and robotic pickers.
Glossary: Key Functions of WES in ASRS Operations:
1. Intelligent Task Scheduling
- Determines which orders to process first based on priority, due dates, and available inventory.
- Ensures that ASRS retrieves high-demand items first, reducing fulfillment times.
2. Dynamic Slotting and Storage Optimization
- Assigns optimal storage locations within ASRS based on real-time demand.
- High-movement items are stored closer to pick points, while low-turnover goods are placed in deeper storage.
3. Automated Picking and Replenishment Coordination
- Synchronizes ASRS retrieval with picking stations to ensure smooth order fulfillment.
- Directs robotic shuttles or cranes to restock shelves as inventory is depleted.
4. Bottleneck Prevention & Load Balancing
- Prevents overloading of ASRS equipment by distributing retrieval tasks across multiple cranes or shuttles.
- Ensures that conveyors, sorters, and picking stations operate at optimal efficiency.
5. Seamless Integration with WMS & ERP
- Pulls order information from WMS to automate ASRS picking tasks.
- Updates real-time inventory levels, reducing stock discrepancies.
6. Workforce & Equipment Synchronization
- Guides human pickers and ASRS machines to work together efficiently.
- Sends alerts for maintenance or system slowdowns, minimizing disruptions.
3. Inventory Management
The process of tracking and managing stock levels, locations, and movements within a warehouse.
Formula for Days of Inventory Outstanding (DIO):
- DIO = (Average Inventory ÷ Cost of Goods Sold) × 365
4. Throughput
The rate at which an ASRS system moves goods.
Formula: Throughput = Total Units Processed ÷ Operational Time
5. Utilization Rate
A measure of how effectively an ASRS system is being used compared to its maximum capacity.
Formula: Utilization Rate = (Actual Usage ÷ Maximum Capacity) × 100
6. Downtime and Uptime
- Downtime: Period when the ASRS is non-operational due to maintenance or failure.
- Uptime: The percentage of time the ASRS is operational and productive.
7. Cycle Time
The time taken to complete one full operation, such as retrieving and placing an item.
Formula: Cycle Time = Retrieval Time + Placement Time
8. Slotting Optimization
The process of organizing inventory in a warehouse to minimize retrieval time and maximize efficiency.
9. SKU Proliferation
The growth in the number of unique products (SKUs) stored in a warehouse, often due to e-commerce expansion.
10. Space Utilization
The percentage of warehouse space effectively used for storage versus unutilized space.
Formula: Space Utilization = (Occupied Storage Space ÷ Total Warehouse Space) × 100
Glossary: KPIs in ASRS Operations
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Metrics to measure the success of ASRS implementation.
1. Order Fulfillment Rate:
Formula: (Orders Delivered On-Time ÷ Total Orders) × 100
ASRS systems help achieve near-perfect rates.
2. Labor Cost Per Pick:
Formula: Total Labor Costs ÷ Total Picks
3. Order Accuracy
The percentage of orders processed without errors.
Formula: Order Accuracy = (Accurate Orders ÷ Total Orders) × 100
4. Energy Efficiency in ASRS
Designing ASRS systems to minimize energy consumption.
5. Return on Investment (ROI)
A measure of the profitability of ASRS investment.
Formula: ROI = (Net Benefits ÷ Total Investment) × 100
Glossary Terms in Warehouse Operations Procedures Related to ASRS
1. Induction
Also referred to as “Stowing,” Induction is the process of placing items into an Automated Storage and Retrieval System (ASRS). Efficient induction ensures accurate inventory tracking and seamless retrieval during order fulfillment.
2. Shipping
Formerly known as “Drop-off,” Shipping refers to the final stage in warehouse operations where items are retrieved from the ASRS and dispatched for delivery. This term is commonly used in logistics to describe outbound processes, ensuring clarity in warehouse communications.
3. Process Standardization
One of the key benefits of implementing ASRS solutions like Rapyuta ASRS is process standardization—ensuring that tasks performed by human workers maintain consistent quality in terms of accuracy and speed. While most automation systems focus on efficiency and workflow optimization, standardizing human-led tasks significantly enhances overall productivity.
Check out our latest white paper explains the error-proofing and efficiency-boosting features of picking stations and their impact on on-site standardization.

4. Full Inventory Count
A Full Inventory Count refers to the process of counting all stored inventory at once. This method provides a comprehensive snapshot of stock levels and is fully compatible with ASRS solutions like Rapyuta ASRS.
5. Cycle Count
Unlike full inventory counts, Cycle Counting is a method where inventory is counted by item category over multiple days. This technique helps distribute the workload while maintaining stock accuracy.
6. Order Wave Planning
Order Wave Planning is a strategy used in warehouse operations to group and release batches of orders for fulfillment based on priority, shipping deadlines, or resource availability. In an ASRS environment, order wave planning helps optimize retrieval sequences, reduce system congestion, and improve overall order processing efficiency.
7. Load Profiling
Load Profiling is the process of analyzing the size, weight, and handling characteristics of stored items to optimize their placement within an ASRS. Proper load profiling ensures that heavier or frequently accessed items are stored in locations that minimize retrieval time and system wear, improving both efficiency and longevity of the ASRS.
8. Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory is a supply chain strategy that minimizes storage needs by ensuring that materials and products arrive exactly when needed for production or order fulfillment. In an ASRS system, JIT inventory management relies on real-time tracking, fast retrieval speeds, and seamless coordination with inbound logistics to maintain lean inventory levels without causing delays.
Conclusion
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS) are reshaping the future of warehouse operations by enhancing efficiency, reducing errors, and enabling scalability. Understanding the key terms and metrics associated with ASRS is the first step to fully harnessing its potential. However, choosing the right solution is just as critical.
Rapyuta ASRS goes beyond standard automation by offering seamless integration with inventory management platforms, intuitive interfaces, and cutting-edge technology designed to optimize workflows. Whether you’re looking to improve picking accuracy, increase throughput, or streamline operations, Rapyuta ASRS is tailored to meet the demands of modern warehouses.
Want to See It in Action?
Book a demo today to experience the unparalleled capabilities of Rapyuta ASRS. From live demonstrations to personalized consultations, discover how it can transform your warehouse operations and drive measurable success.
FAQS
1. What is an Automated Storage and Retrieval System (ASRS)?
An ASRS is a computer-controlled warehouse solution that automatically stores and retrieves goods from predefined locations. It reduces manual labor, increases storage density, and improves picking accuracy.
2. Can Rapyuta ASRS integrate with existing Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)?
Yes, Rapyuta ASRS offers seamless API integration with major WMS platforms. This ensures real-time inventory updates, smoother workflows, and faster deployment without the need to replace your current systems.
3. What are unit load ASRS and how are they used in logistics?
Unit load ASRS refers to systems that handle large, pallet-sized loads. They are ideal for bulk storage and retrieval in industries like manufacturing, automotive, and third-party logistics (3PL), where high-capacity handling is essential.
4. What are vertical lift modules (VLMs) and how do they compare to Rapyuta ASRS?
VLMs are enclosed systems with vertically arranged trays that move the operator. While ideal for space-saving, they are typically static. In contrast, Rapyuta ASRS offers mobile robots, dynamic bin management, and greater scalability for high-throughput environments.
5. How does bin management work in Rapyuta ASRS?
Rapyuta ASRS uses intelligent fleet control and dynamic bin removal. Robots can temporarily relocate front bins to access deeper items, enabling tight bin packing while maintaining accessibility and reducing idle time.
6. Is ASRS suitable for 3PL or multi-client warehouses?
Yes. Rapyuta ASRS is ideal for 3PL operations, supporting client-specific bin mapping, secure data segregation, and real-time tracking—making it easy to manage multiple customer inventories from one platform.
7. What is the role of fleet control in warehouse robotics?
Fleet control is the system that manages the movement and coordination of multiple robots. In Rapyuta ASRS, it ensures efficient traffic flow, avoids collisions, and optimizes task assignments to maximize throughput.



